In recent years, blockchain technology has moved from a niche concept associated with cryptocurrencies to a mainstream subject of interest across various industries. Blockchain is known for its potential to transform data and transactions in finance and supply chain management. But what exactly is blockchain technology, and why is it generating so much buzz? This article provides a comprehensive overview of blockchain technology, including its principles, applications, and implications.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
At its core, blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers to ensure the security and transparency of the data. This technology underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum but has applications far beyond digital currencies.
The Basics of Blockchain
A blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks, each containing data. A continuous chain arises by linking these blocks successively. Each block includes a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a unique identifier called a cryptographic hash, which links it to the previous block. This linkage creates an immutable record of all transactions.
Critical components of a blockchain include:
- Blocks: These are the basic units of data storage in a blockchain. Each block contains a set of transactions, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block’s hash.
- Chain: The blocks create a chain linearly. Each block’s hash is based on the data in the block and the previous block’s hash, making it almost impossible to alter the data without changing every subsequent block.
- Nodes: These are individual computers that participate in the blockchain network. Each node maintains a copy of the blockchain and contributes to verifying and validating transactions.
- Consensus Mechanisms: These protocols agree on blockchain state. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
How Blockchain Works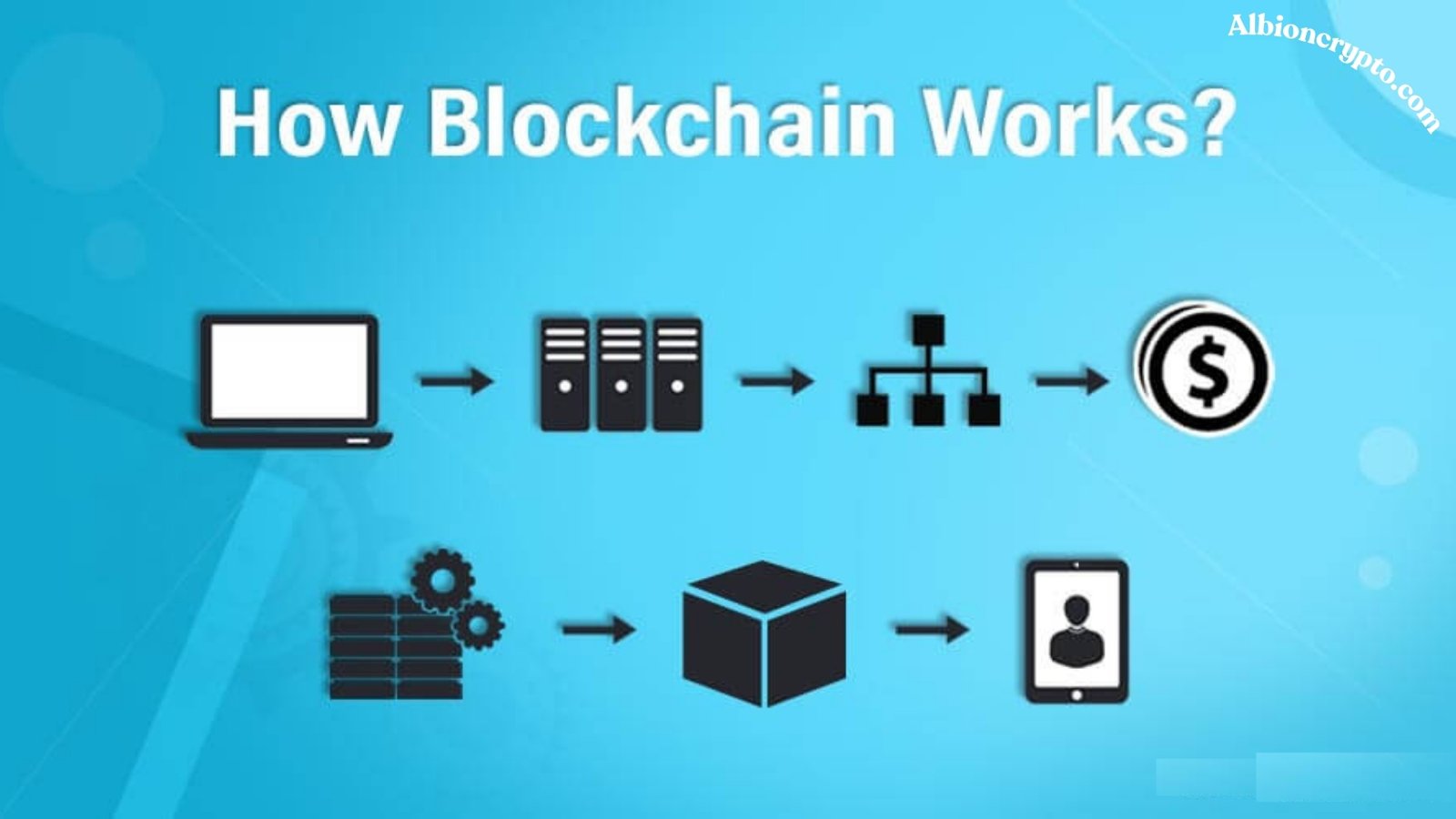
The process of adding a new block to the blockchain involves several steps:
- Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction, which is then broadcast to the network of nodes.
- Transaction Validation: Nodes verify the transaction using pre-set rules. This process involves checking the transaction’s authenticity and ensuring the sender has the necessary balance or permissions.
- Block Creation: Whether mining in PoW systems or validation in PoS systems, the goal is to compile all valid transactions into a new block.
- Block Addition: Each new block is broadcast to all network nodes. Each node verifies the block and its transactions. The block is deemed valid and added to the existing blockchain.
- Consensus: The network reaches a consensus on the validity of the new block. Once consensus is achieved, the block becomes a permanent part of the blockchain.
- Immutability: The hash links the current block to the preceding block, making data changes practically impossible without altering all blocks.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single entity controls the data, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes. This decentralization enhances security and reduces the risk of single points of failure.
- Transparency: All transactions recorded on a blockchain are visible to all participants in the network. This transparency helps build trust and accountability.
- Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure data. A cryptographic hash links each block to the previous block, making it tamper-resistant.
- Immutability: Once data is added to a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity of the data.
- Consensus: Blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms to agree on the validity of transactions and blocks. This process ensures that all participants in the network have a consistent view of the data.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
While blockchain is best known for its role in cryptocurrencies, its potential applications extend beyond digital currencies. Here are some notable examples:
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are perhaps the most well-known applications of blockchain technology. They rely on blockchain to manage and record transactions in a decentralized manner without the need for intermediaries like banks.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains. By recording every step of a product’s journey on a blockchain, companies can track its origin, verify authenticity, and ensure that it meets quality standards.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. When specific criteria are met, they automatically enforce contracts. Smart contracts can streamline processes in various industries, including real estate and finance.
Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain can securely store and share patient data. It allows for creating a unified, tamper-proof record of patient information, which can improve the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment plans while safeguarding patient privacy.
Voting Systems
Blockchain has the potential to improve the integrity of voting systems. A blockchain can record votes transparently and tamper-proof, preventing fraud and ensuring accurate counting.
Financial Services
Blockchain is studying cross-border payments, trade finance, and digital identity verification beyond cryptocurrencies. Its ability to provide secure and transparent transactions makes it a valuable tool for modernizing financial systems.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promising potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges and limitations:
Scalability
Many blockchain networks struggle with scalability issues. As the number of transactions grows, the blockchain can become congested, leading to slower processing times and higher transaction fees.
Energy Consumption
Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (used by Bitcoin) require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption. This has raised concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Uncertainty about regulations can hinder adoption and innovation, as businesses and individuals may be wary of potential legal and compliance issues.
Privacy Concerns
While blockchain provides transparency, it can also raise privacy concerns. The visibility of transaction data on public blockchains may lead to unintended exposure of sensitive information.
Interoperability
Different blockchain networks often operate in isolation, making transferring data and assets between them challenging. Efforts are underway to develop solutions for improving interoperability between blockchains.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at addressing its current challenges and expanding its applications. Sharding, layer two solutions, and energy-efficient consensus mechanisms are examined for scalability and sustainability.
Moreover, integrating blockchain with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), holds the potential to create new and transformative use cases. As blockchain technology evolves, its impact on various industries will likely grow, driving greater efficiency, transparency, and security.
In Summary
Blockchain technology represents a significant shift in how we manage and record data. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature offers numerous benefits across various domains, from finance to supply chain management. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and innovative applications suggest a bright future for blockchain technology. As we continue to explore and refine this technology, it is clear that blockchain has the potential to reshape industries and create new opportunities for a more connected and transparent world.
FAQs
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash linking it to the previous block. This structure ensures data security, transparency, and immutability, making it nearly impossible to alter recorded information without detection.
How does blockchain differ from traditional databases?
Unlike traditional centralized databases controlled by a single entity, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes (computers). Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain and participates in verifying transactions. This decentralization enhances security, eliminates single points of failure, and provides transparency since all participants can view the recorded transactions.
What are some real-world applications of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency?
Blockchain has diverse applications across industries: supply chain management for tracking product authenticity and origin, smart contracts that automatically execute when conditions are met, healthcare for secure patient data sharing, voting systems to prevent fraud, and financial services for cross-border payments and trade finance.
What are the main challenges facing blockchain technology?
The primary challenges include scalability issues leading to slower transaction processing as networks grow, high energy consumption (especially with Proof of Work mechanisms), evolving regulatory uncertainty, privacy concerns due to transaction transparency on public blockchains, and interoperability difficulties between different blockchain networks.
Is blockchain technology secure and immutable?
Yes, blockchain is highly secure due to cryptographic techniques that link each block to the previous one. Once data is added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable—it cannot be altered or deleted without changing all subsequent blocks, which would require consensus from the entire network. This makes blockchain extremely resistant to tampering and fraud.


